Understanding Types of Scoliosis Curvature
Navigating scoliosis can be challenging, but understanding different spinal curvatures can provide clarity. This guide offers a clear look at how these curvatures affect your spine and health, helping you recognize symptoms and explore treatment options.
What is Scoliosis?
Scoliosis is the spine curves sideways, forming a “C” or “S” shape instead of a straight line. This usually happens during growth spurts in childhood or adolescence. In adults the scoliosis happened with degeneration. The curvature can cause uneven shoulders, a tilted waist, and or hips shifted. According to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) and the Scoliosis Research Society (SRS), understanding scoliosis helps in finding the right treatment and managing the condition to improve overall well-being.
Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis (AIS)
AIS is a type of scoliosis with an “unknown cause” that typically affects children ages 10-18, especially girls. It is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Studies suggest that the abnormal curvature of the spine might be related to hormonal changes, unusual bone or muscle growth, or nervous system issues, though the exact cause is still not fully known.
Congenital Scoliosis
This condition is present from birth, caused by incomplete development of the spine while the baby is in the womb. This means that the spine doesn’t form properly during pregnancy, leading to a curvature that is noticeable early in life.
Neuromuscular Scoliosis
Neuromuscular scoliosis occurs due to nerve or muscle conditions like cerebral palsy or muscular dystrophy. These conditions weaken the muscles around the spine, leading to an imbalanced curvature.
Degenerative Scoliosis
This is also known as “adult onset scoliosis”, it occurs due to the degeneration of the spine with aging. This type often results from the wear and tear on the spinal discs and joints, causing a gradual curvature.
Early Onset Scoliosis
Early Onset Scoliosis occurs in children younger than 10 years old. This type of scoliosis develops before the child’s growth spurt and can be more challenging to manage.
Dextroscoliosis
Dextroscoliosis is when the spine curves to the right side of the body. This can cause uneven shoulders and rib prominence.
Levoscoliosis
Levoscoliosis is when the spine curves to the left side of the body. This leads to uneven shoulders and a tilted waist.
Symptoms and Signs of Scoliosis
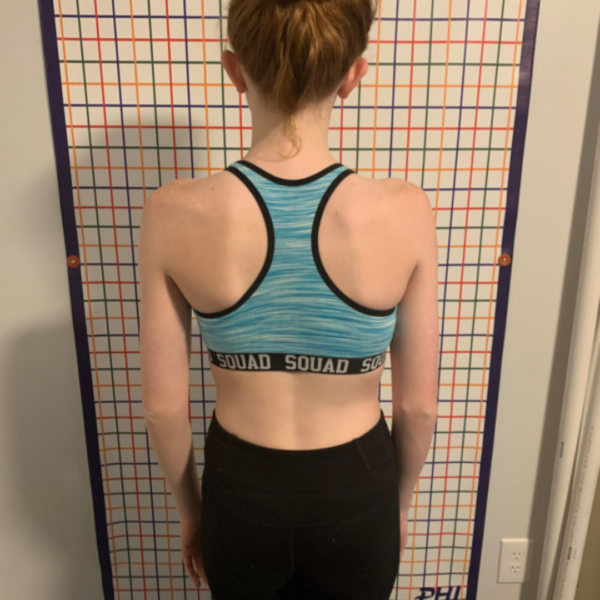
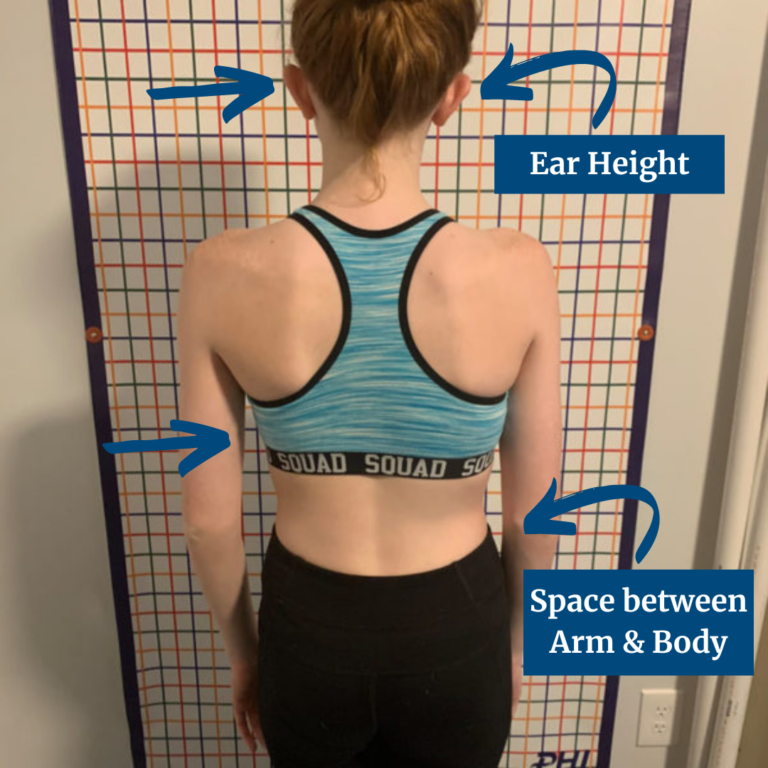
Early detection of scoliosis can lead to better treatment outcomes. Look out for signs like uneven shoulders, one shoulder blade sticking out more than the other, or uneven hips. You might also notice that your waist appears uneven or that your ribs bulge out more on one side when you bend forward. In some cases, scoliosis can cause back pain and, if severe, affect breathing. If you spot any of these signs, it’s important to seek medical advice early to ensure effective treatment and prevent further complications.
How is Scoliosis Diagnosed:
Methods and Procedures
Scoliosis requires precise diagnosis for effective management. Understanding the diagnostic methods and procedures is crucial for timely and accurate detection.
Initial Physical Examination
Visual Inspection
The physician looks for asymmetry in the shoulders, waist, and hips.
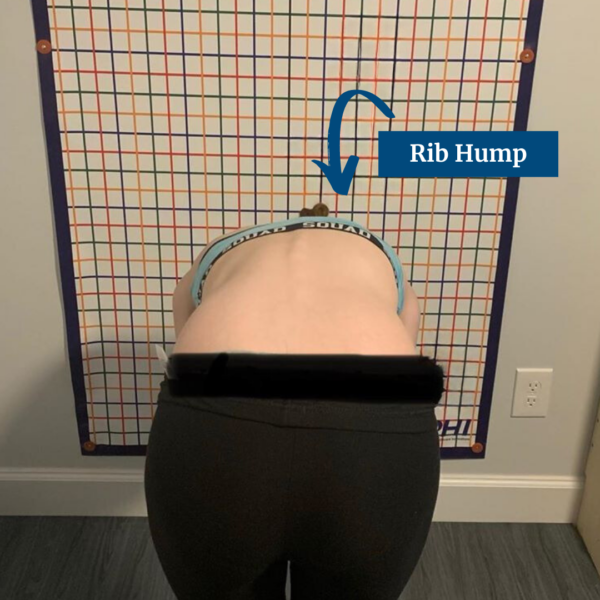
Adam’s Forward Bend Test
The patient bends forward, allowing the doctor to observe any rib hump or spinal curve.
Medical History Review
Family History
Inquiry about any family history of scoliosis or other spinal conditions.
Symptoms and Onset
Discussion of symptoms such as back pain, uneven shoulders, or noticeable curvature, and when they first appeared.
Imaging Tests
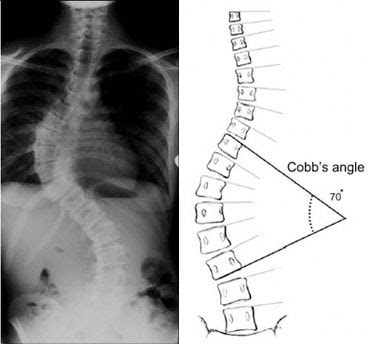
X-Rays
The most common imaging test, providing a clear picture of the spine’s structure. X-rays help measure the degree of curvature (Cobb angle).
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
Used if there are neurological symptoms or if the doctor suspects an underlying condition affecting the spinal cord.
CT Scan (Computed Tomography)
Occasionally used for detailed images when complex spinal issues are suspected.
Scoliometer
A scoliometer is a small device used during the physical examination to measure the angle of trunk rotation (ATR). It helps assess the severity of scoliosis.